“Capybaras are the world’s largest rodents, weighing up to 70 kilograms.” “They can hold their breath underwater for up to five minutes.” “These social creatures often live in herds of 10 to 20 members, but during dry seasons, groups can swell to over 100 individuals.”
If you’ve ever seen a picture of a capybara lounging in a hot spring surrounded by other animals, you probably thought: What is this adorable, calm-looking creature? Capybaras have gained global popularity not only for their size and unique appearance but also for their peaceful personalities and fascinating lifestyle.
The Largest Rodent in the World
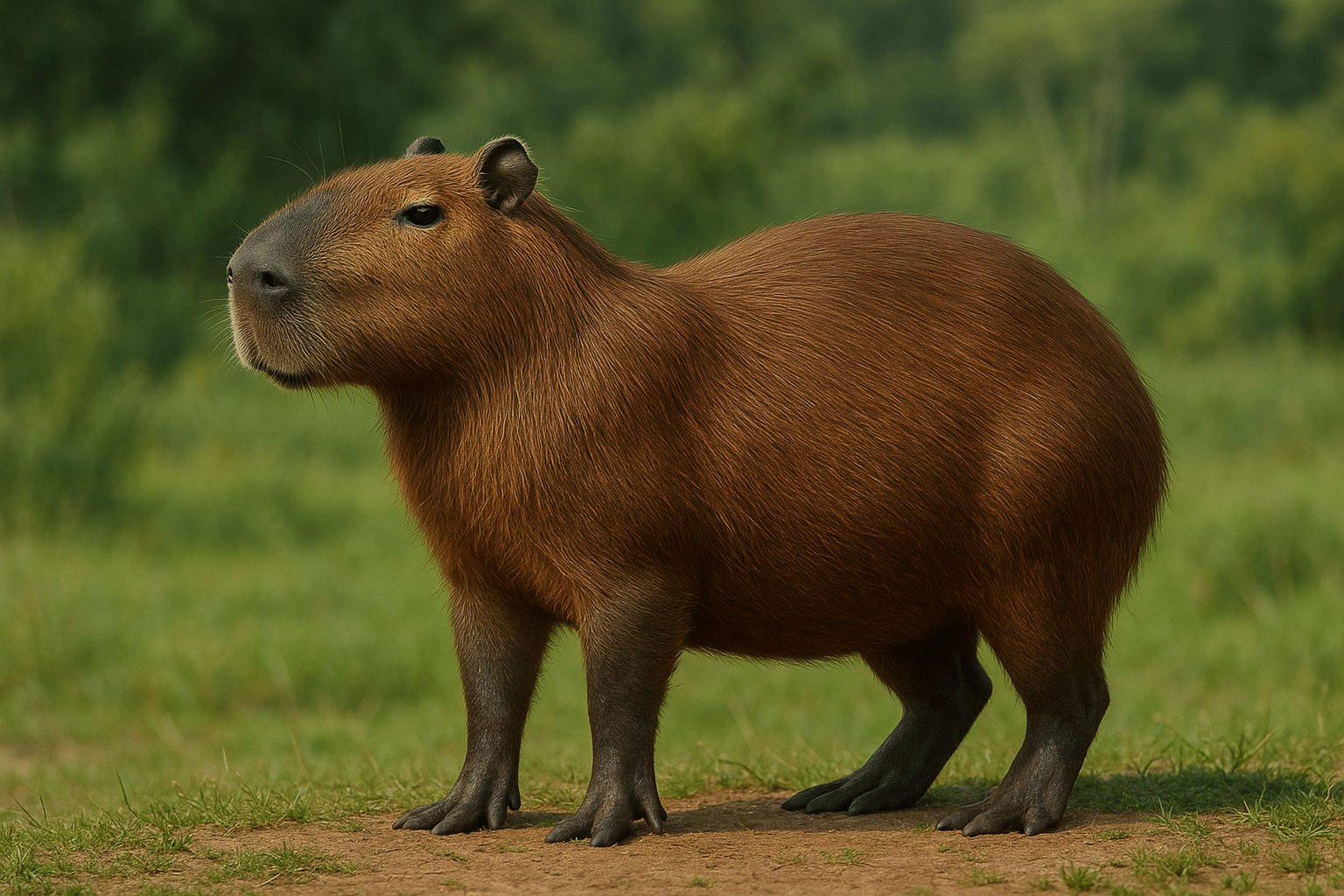

When you think of rodents, you might imagine small animals like mice or squirrels. But capybaras are in a league of their own. Measuring up to 130 centimeters (4.3 feet) in length and standing 50–60 centimeters (1.6–2 feet) tall at the shoulder, they are by far the largest living rodents.
An adult capybara typically weighs between 35 and 70 kilograms (77–154 pounds), though some particularly large individuals can exceed 90 kilograms. Despite their size, they are agile on both land and water, and their barrel-shaped bodies are perfectly suited to their semi-aquatic lifestyle.
Semi-Aquatic Masters
One of the most remarkable adaptations of the capybara is its ability to thrive both on land and in water. Their eyes, ears, and nostrils are positioned high on their heads, allowing them to remain mostly submerged while still keeping watch for predators.
Capybaras are excellent swimmers, capable of holding their breath underwater for up to five minutes. They use water not only as an escape route from threats but also as a way to regulate body temperature in hot climates. In fact, they often spend hours lounging in rivers, lakes, or marshes to stay cool.
Social Butterflies of the Animal Kingdom
Capybaras are highly social creatures that live in groups. A typical group consists of 10–20 members, but in the dry season—when water sources become limited—groups can merge to form super-herds of up to 100 individuals.
These herds are usually led by a dominant male, accompanied by several females, their offspring, and subordinate males. Group living provides them with safety in numbers, better access to resources, and opportunities for social grooming—a bonding activity where they nibble and clean each other’s fur.
Peaceful Coexistence with Other Animals
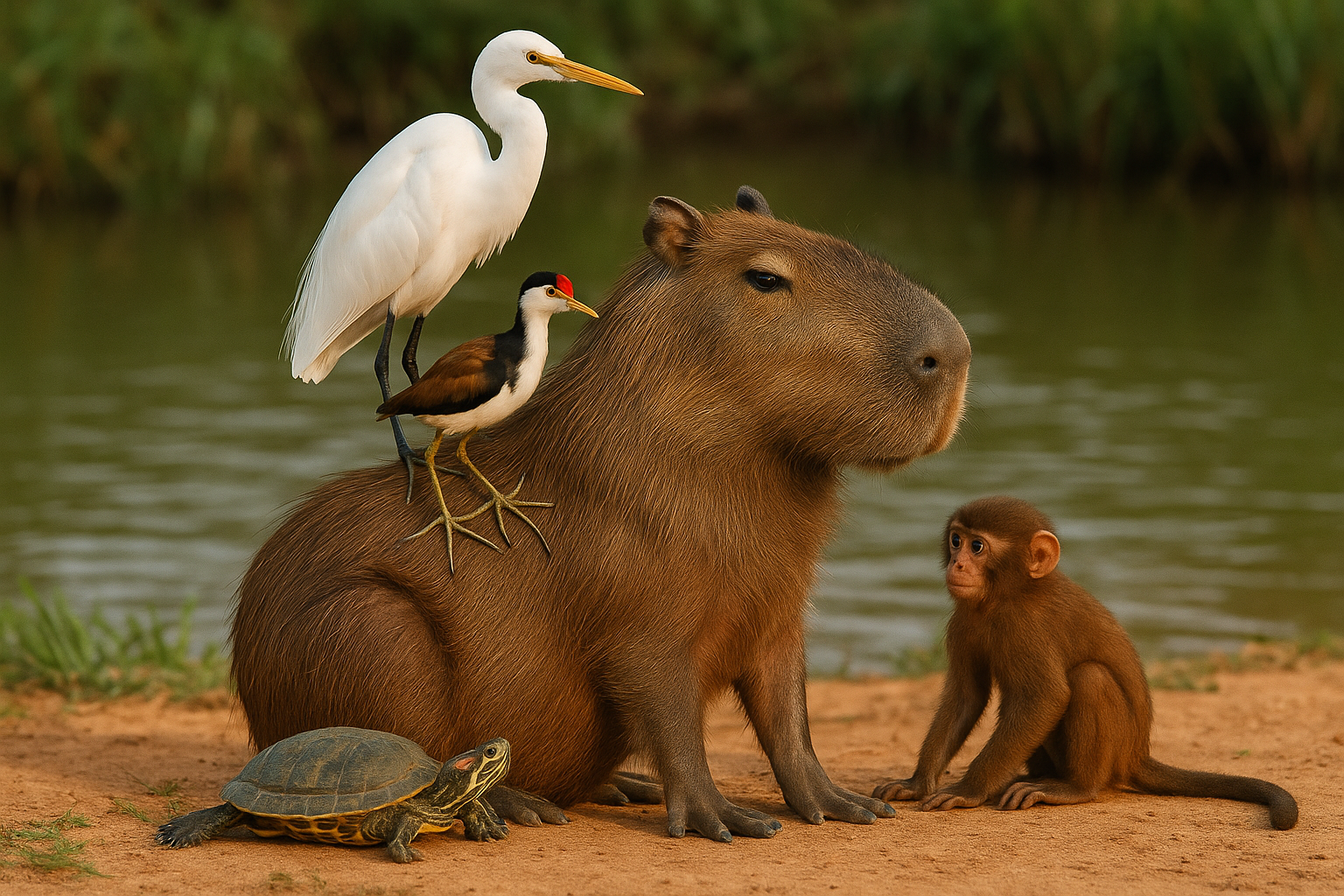

Capybaras are famous for their calm demeanor. Birds like egrets and jacanas perch on their backs to feed on insects, while monkeys and even turtles are often seen hanging out around them without fear. This peaceful coexistence has turned them into internet celebrities in wildlife photography and memes.
Herbivorous Diet

Capybaras are strict herbivores, feeding mainly on grasses, aquatic plants, reeds, and sometimes fruit. They have an interesting digestive adaptation: they practice coprophagy—eating their own feces—to extract every possible nutrient from their fibrous diet.
Their continuously growing teeth help them chew through tough vegetation without wearing them down. During the dry season, when grass is scarce, they may rely more on aquatic plants and reeds to survive.
Habitat and Distribution
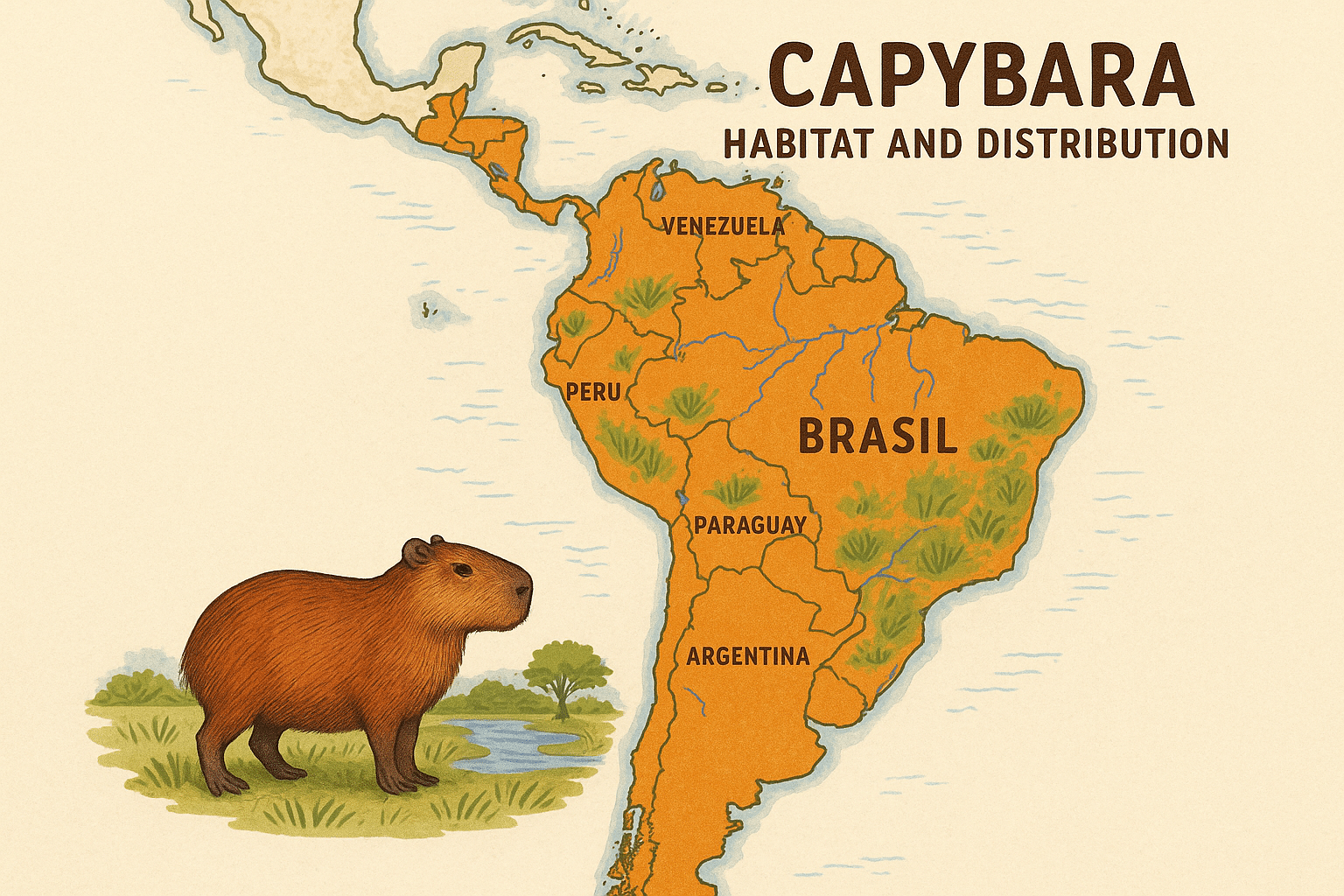
Capybaras are native to South America and are found in countries like Brazil, Venezuela, Colombia, Argentina, Paraguay, and Peru. They prefer environments near bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, marshes, and wetlands where they can easily escape predators and find abundant food.
They are adaptable creatures and can survive in grasslands, savannas, and even human-modified landscapes as long as there’s a reliable water source.
Reproduction and Family Life
Breeding seasons vary depending on location. In some areas, capybaras breed year-round, while in others, mating peaks during the rainy season.
After a gestation period of about 150 days, females give birth to a litter of 4–5 pups (though litters can range from 1 to 8). The young are precocial, meaning they are born fully furred, with open eyes, and able to eat grass within a week.
One of the most fascinating aspects of capybara parenting is alloparenting where other females in the group help care for and protect the young, regardless of whether they are their own offspring.
Unique Adaptations
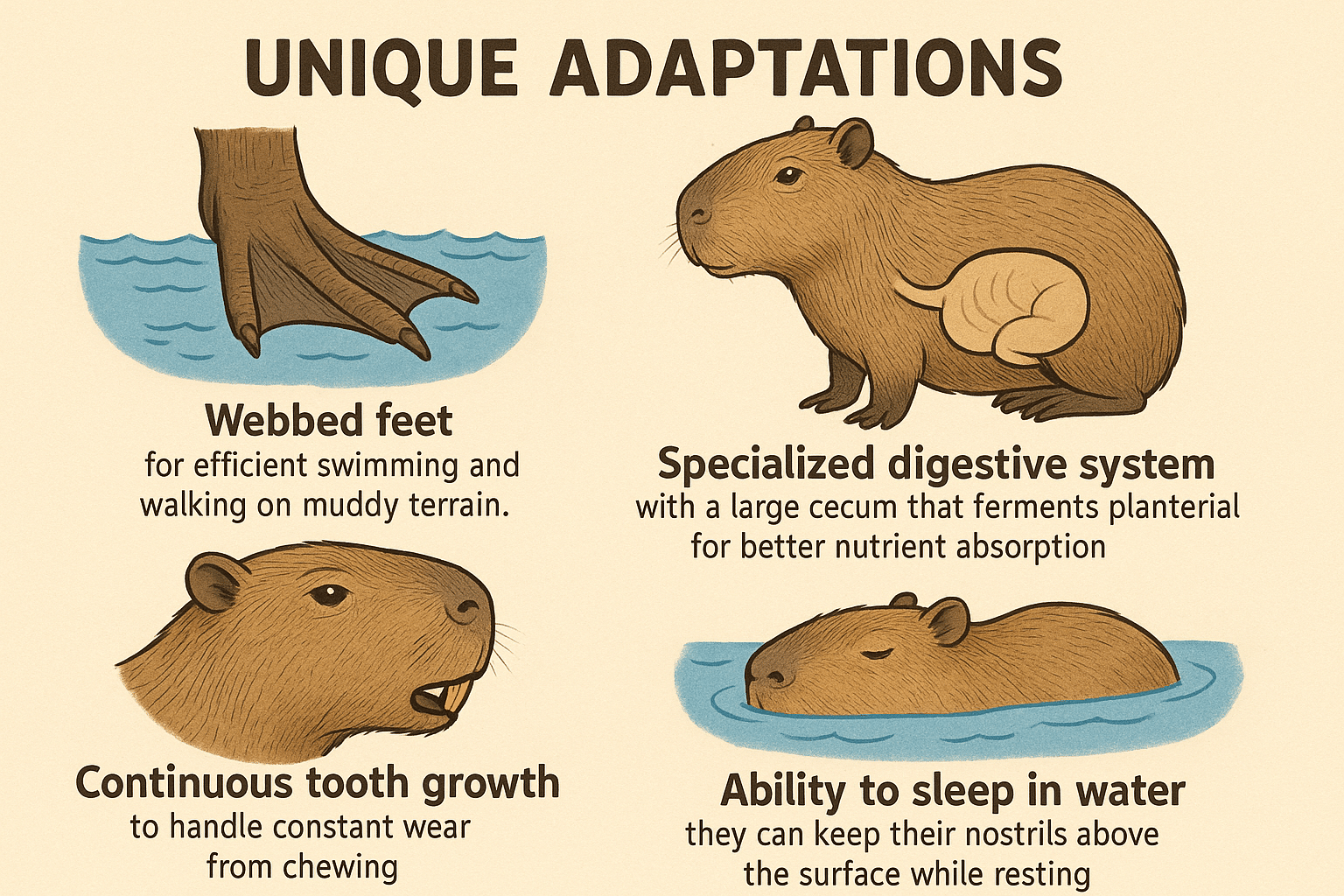
Capybaras have several traits that help them thrive in their environment:
-
Webbed feet – for efficient swimming and walking on muddy terrain.
-
Specialized digestive system – with a large cecum that ferments plant material for better nutrient absorption.
-
Continuous tooth growth – to handle constant wear from chewing.
-
Ability to sleep in water – they can keep their nostrils above the surface while resting.
Predators and Threats

Despite their size, capybaras are prey for several predators, including jaguars, pumas, ocelots, anacondas, caimans, and even large birds of prey. Humans also hunt them for their meat and hide.
To avoid danger, capybaras rely on their swimming ability, group vigilance, and sharp senses. When threatened, they will dive underwater and can remain hidden for minutes before resurfacing at a safe distance.
Conservation Status
Currently, capybaras are listed as Least Concern by conservation organizations due to their wide range and stable population. However, habitat destruction, overhunting, and climate change can pose local threats. In some countries, they are farmed for meat and leather, while in others, they are protected by law.
When creativity runs dry, this online animal name generator makes it easy to discover animal names in just a few clicks.
Capybaras in Culture and the Internet

In recent years, capybaras have become viral sensations on social media. Memes, videos, and pictures show them lounging peacefully with other animals or enjoying baths in hot springs. In Japan, they are a major attraction in zoos and hot spring parks, especially in winter when they soak in steaming water surrounded by floating yuzu fruits.
They have also appeared in children’s books, cartoons, and even songs, becoming symbols of calmness and friendliness.
Fun and Lesser-Known Facts About Capybaras

-
They can run as fast as a horse in short bursts to escape predators.
-
Capybaras are crepuscular, meaning they are most active during dawn and dusk.
-
They mark their territory with scent glands located on their noses and anal regions.
-
In some rural areas, they are kept as pets, though they require plenty of space, water access, and companionship.
-
Their scientific name, Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, means “water pig.”
Why People Love Capybaras

From their calm personalities to their adorable looks, capybaras embody a unique blend of charm and resilience. They remind us of the value of living peacefully, adapting to our surroundings, and cherishing community bonds.
Whether in the wild wetlands of South America or featured in viral internet posts, capybaras continue to fascinate animal lovers around the world.



